
|
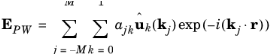 ,
,
|
1
|
|
2
|
In the Select Physics tree, select Optics>Wave Optics>Electromagnetic Waves, Frequency Domain (ewfd).
|
|
3
|
Click Add.
|
|
4
|
Click
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Click
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
Click to expand the Layers section. In the table, enter the following settings:
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
|
10
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
Select the object c1 only.
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
Locate the Selections of Resulting Entities section. Select the Resulting objects selection check box, to simplify later selection of the nanorods.
|
|
9
|
|
10
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
In the tree, select Built-in>Air.
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
In the Model Builder window, under Component 1 (comp1) click Electromagnetic Waves, Frequency Domain (ewfd).
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
From the Gaussian beam type list, choose Plane wave expansion. This makes the Gaussian beam background field be a true solution to the Helmholtz equation.
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
|
10
|
|
11
|
Locate the Components section. From the Electric field components solved for list, choose Out-of-plane vector.
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
Locate the Electric Displacement Field section. From the Electric displacement field model list, choose Drude-Lorentz dispersion model.
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
In the Model Builder window, under Component 1 (comp1) click Electromagnetic Waves, Frequency Domain (ewfd).
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
7
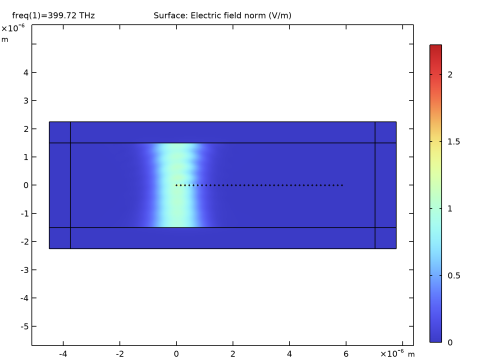
|