You are viewing the documentation for an older COMSOL version. The latest version is
available here.
The Metallurgical Phase node defines a phase. Depending on the settings at the physics interface level and the space dimension where the physics interface is used, the phase node will contain different sections, see
Table 4-2.
Provide the Volume reference temperature Tref for the phase. This is the temperature at which the thermal strain is zero for the phase.
Define the Initial phase fraction for the phase. This fraction should be a value between zero and one, and you have to ensure that the initial phase fractions for all the phases in your analysis sum to one.
If you select Compute transformation times, you can store the times
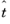
and temperatures
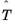
during an analysis, corresponding to reaching specified target phase fractions. Enter a list of
Target phase fractions 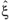
in the table. Whether transformation times and temperatures are recorded depends on if the phase fraction is increasing or decreasing during the analysis. Select
Decreasing phase fraction if the phase fraction is expected to reach the specified target values when it is decreasing. With
Compute transformation times selected, and in the case a phase fraction is increasing over time, you can select
Compute time to completion. Enter the
Completion rate, that is, a rate of phase formation low enough that the formation of the phase can be considered complete.
From the Phase material list, you select the material that defines the material properties for the phase. This section is visible only if at least one of the
Compute effective thermal properties or the
Compute effective mechanical properties check boxes has been selected at the physics interface level. You can create a material at the component level by using
Create Phase Material. When you define material properties for the phase,
From material will refer to the material that you have selected from the
Phase material list.
If the Compute effective thermal properties has been selected at the physics interface level, you must define the thermal properties for the phase. The default
Thermal conductivity k,
Density ρ, and
Heat Capacity at constant pressure Cp, use values
From material. The
From material option refers to the selected material from the
Phase Material list. For
User defined, enter values or expressions for these properties.
If the Compute effective electromagnetic properties has been selected at the physics interface level, you must define electromagnetic properties for the phase. The default
Relative permeability μr,
Electrical conductivity σ, and
Relative permittivity εr, use values
From material. The
From material option refers to the selected material from the
Phase Material list. For
User defined, enter values or expressions for these properties.
If the Compute effective mechanical properties has been selected at the physics interface level, you must define mechanical properties for the phase. The default Young’s modulus
E and Poisson’s ratio
ν use values
From material. For
User defined, enter values or expressions for these properties.
If Enable thermal strains has been selected at the physics interface level, you have to define the
Secant coefficient of thermal expansion α for the phase. By default, the value is taken
From material. For
User defined, enter a value or expression.
If Enable phase plasticity has been selected at the physics interface level, you have to define the plastic behavior of the phase. The default
Initial yield stress σys0 uses a value
From material. For
User defined, enter another value or expression for initial yield stress. Initial yield stresses for phases can be weighted differently. This is useful when initial yield stresses for the phases in the model are very different. Select a
Weight factor for yield stress —
Linear,
Geijselaers, or
User defined. If
Geijselaers is selected, you also need to specify a
Soft phase, which is considered plastically soft in comparison to this phase. You should typically use this to give a stronger weight to martensite (hard) in relation to austenite (soft).
Select the Isotropic hardening model —
Perfectly plastic,
Linear, or
User defined to define the hardening behavior of the phase.
Specify the Isotropic hardening modulus ETiso. The default value is taken
From material.
For User defined, enter another value or expression for the modulus. If a
User defined isotropic hardening modulus is selected, you have to select the
Hardening function. By default, the value is taken
From material.
For User defined, enter a value or expression for the
hardening function. The expression can depend, for example, on the equivalent plastic strain in the phase.
|
|
In a phase (phase4) of an Austenite Decomposition interface ( audc), the equivalent plastic strain is audc.phase4.epe.
|