Use this node to model inflow of water vapor through a virtual domain, at inlet boundaries of moist air and hygroscopic porous medium domains. The upstream moisture conditions (either vapor concentration custr, or vapor mass fraction
ωustr, or relative humidity
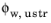
and temperature
Tustr) are known at the outer boundary of the virtual domain. The inflow condition is often similar to a moisture content condition. However using this condition the upstream vapor concentration is not strictly enforced at the inlet. The higher the flow rate, the smallest difference between the inlet and upstream moisture content. In case of moisture sources or moisture constraints close to the inlet boundary, the inflow condition induces a moisture profile that approaches to the moisture profile that would be obtained by computing the solution in the virtual domain upstream the inlet.
When the Diluted species option is selected in the
Mixture type for moist air list, this boundary condition estimates the moisture flux through the inlet boundary from a Danckwerts condition on the vapor concentration:
When the Concentrated species option is selected in the
Mixture type for moist air list, this condition is rewritten as:
When Specify is set to
Relative humidity in the
Specify list, set both the
Upstream temperature Tustr and the
Upstream relative humidity 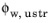
from which the upstream vapor concentration and the vapor mass fraction can be defined:
For User Defined, enter values or expressions. Else, select any available input (like
Ambient temperature defined in an
Ambient Properties node under
Definitions).
Alternatively, choose Vapor concentration in the
Specify list, and set directly a value or expression for the
Upstream vapor concentration custr.
Finally, choose Vapor mass fraction in the
Specify list to set a value or expression for the
Upstream vapor mass fraction ωustr.