In domains, the total heat flux, tflux, is the sum of the conductive and convective heat fluxes. For accuracy reasons the radiative heat flux is not included.
For fluid domains (for example, Fluid), the total heat flux is defined as:
The conductive heat flux variable, dflux, is evaluated using the temperature gradient and the effective thermal conductivity:
In the general case keff is the thermal conductivity,
k.
For heat transfer in fluids with turbulent flow, keff =
k +
kT, where
kT is the turbulent thermal conductivity.
For heat transfer in porous media, keff is the effective conductivity computed from the solid and fluid conductivities.
The turbulent heat flux variable, turbflux, enables access to the part of the conductive heat flux that is due to turbulence.
The convective heat flux variable, cflux, is defined using the internal energy,
Ei:
where H is the enthalpy defined in
Equation 4-5.
The convective heat flux may be oriented in the opposite direction of the velocity field’s direction, when the internal energy, Ei, has a negative value. This happens when the sensible enthalpy (variation from reference enthalpy
Href) is negative.
Href is set to 0 J/kg at
pref (1 atm),
cref (0 mol/m
3), and
Tref (293.15 K) in COMSOL Multiphysics. See
Thermodynamic Description of Heat Transfer for details.
In participating media, the radiative heat flux, qr, is not available for analysis on domains because it is more accurate to evaluate the radiative heat source
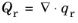
.
The total energy flux, teflux, is defined when viscous dissipation is enabled: