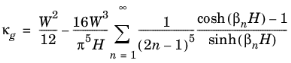The H2 Gas Flow Channel and
O2 Gas Flow Channel nodes specify domains with only a
Gas Phase node being active.
This node will be available if the Include gas phase diffusion check box or the
Use Darcy’s law for momentum transport check box has been selected in the corresponding
Gas Mixture section on the interface top node.
If the Include gas phase diffusion check box has been selected, there are no settings on this node. The gas diffusivity defined in the
Gas Phase node.
If the Use Darcy’s law for momentum transport check box has been selected, the
Gas permeability is defined in this node.
The Gas permeability option of
Straight channels can be used to specify the permeability for a straight channel with a uniform cross section, for which analytical correlations exist for expressing the flow rate as proportional to the volumetric flow. For a rectangular cross section, with height
H and width
W, the corresponding Darcy permeability
κg (derived by Boussinesq in 1868) is
with βn being a help variable equal to