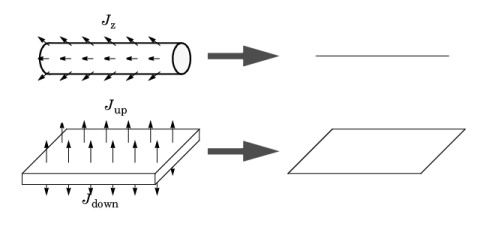
For a 1D component this node adds a single out-of-plane molar flux J0,z,i for species
i. For a 2D component two fluxes can be prescribed for each species;
J0,u,i for the upside of the domain, and
J0,d,i for the downside of the domain.
where Sopf,i is the out-of-plane source for species
i
where kc is a mass transfer coefficient and
cb is the bulk concentration, the typical concentration far into the surrounding exterior domain. The prescribed flux,
J0, can include any arbitrary user-specified expressions. It can be a constant or a function of a dependent variable or independent variables.
For 1D components, enter the cross-sectional perimeter P
c to get the out-of-plane flux
The default value of Pc is the circumference. Either keep the default value, for a circular cross-section shape, or edit the value to get a user-defined shape of the out-of-plane cross-section.
The available flux type options are General inward flux and
External convection. Select the
Species check box for the species for which to specify the flux, and enter a value or expression for the inward flux in the corresponding field. Use a minus sign when specifying a flux directed out of the system. To use another boundary condition for a specific species, click to clear the check box for that species.
Set Flux type to
External convection to prescribe a flux to or from an exterior domain (not modeled) assumed to include convection. The exterior can for example include a forced convection to control the temperature or to increase the mass transport. In this case the prescribed mass flux corresponds to
where kc is a mass transfer coefficient and
cb is the bulk concentration, the typical concentration far into the surrounding exterior domain.
The available options are General inward flux and
External convection. The settings are the same as for the
Upside Inward Flux section.