The Periodic Flow Condition splits its selection into a source group and a destination group (the
Destination Selection section is optional). Fluid that leaves the domain through one of the destination boundaries enters the domain through the corresponding source boundary. This corresponds to a situation where the geometry is a periodic part of a larger geometry. If the boundaries are not parallel to each other, the velocity vector is automatically transformed.
No input is required when Compressible flow (Ma<0.3) is selected for
Compressibility under the
Physical Model section for the physics interface. Typically when a periodic boundary condition is used with a compressible flow, the pressure is the same at both boundaries and the flow is driven by a volume force.
This section is available for specifying the destination boundaries, if needed, when the Manual Destination Selection option is selected in the context menu for the
Periodic Flow Condition node. You can only select destination boundaries from the union of all source and destination boundaries.
This section is available when Incompressible flow is selected for
Compressibility under the
Physical Model section for the physics interface.
The Flow Condition at the boundary is specified through a value or expression for either the
Pressure difference,
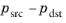
, or the
Mass flow,
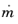
. The mass flow option ensures a pressure difference is achieved across the source and destination boundaries. This pressure difference can, for example, drive the fully developed flow in a channel.
To set up a periodic boundary condition, both boundaries must be selected in the Periodic Flow Condition node. COMSOL Multiphysics automatically assigns one boundary as the source and the other as the destination. To manually set the destination selection, a
Destination Selection subnode is available from the context menu (by right-clicking the parent node) or from the
Physics toolbar,
Attributes menu. All destination sides must be connected.
To display this section, click the Show More Options button (

) and select
Advanced Physics Options in the
Show More Options dialog box. For information about the
Orientation of Source section, see
Orientation of Source and Destination in the
COMSOL Multiphysics Reference Manual.
This section appears if the setting for Transform to intermediate map in the
Orientation of Source section is changed from the default value,
Automatic, and
Advanced Physics Options is selected in the
Show More Options dialog box. For information about the
Orientation of Destination section, see
Orientation of Source and Destination in the
COMSOL Multiphysics Reference Manual.
To display this section, click the Show More Options button (

) and select
Advanced Physics Options in the
Show More Options dialog box. For information about the
Mapping Between Source and Destination section, see
Mapping Between Source and Destination in the
COMSOL Multiphysics Reference Manual.