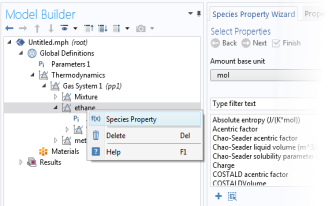
A Species Property is used to define and compute a pure species property. The available properties consist of both parameters and functions. Some examples of available parameters are molar mass, Lennard Jones diameter, and dipole moment. Some examples of available functions are density, enthalpy, heat capacity, and viscosity. The property functions created are either dependent on temperature alone, or both on temperature and pressure. For all property functions, the first order derivative with respect to temperature and, when applicable, with respect to pressure are automatically defined. The second-order derivatives with respect to temperature and pressure are available for property functions of density and molar volume.
The Species Property Wizard contains the following steps:
First use the Amount base unit list to define the base unit. Select
mol or
kg.
Click the Next button (

) to proceed to the next step, selecting the phase.
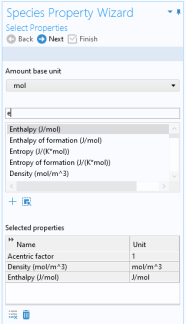
Click the Next button (

) to proceed to the next step, selecting the species.
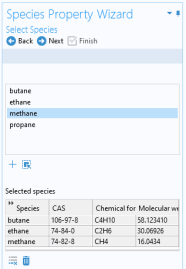
Select one or more of the species available in the thermodynamic system and use the Add Selected button (
) to add them to the
Selected species table. One property function is created for each of the selected species.
Click the Next button (

) to proceed to the Species Property Overview in the wizard.
Selecting a Species Property node shows the settings for such property.
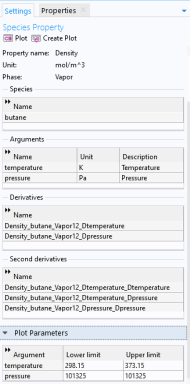
You can use the Parameter name or
Function name fields to specify or change the name of a parameter or a function. The section also provides information about the property type and the species it is defined for.
Apply a Lower limit and an
Upper limit for each argument, and click the
Plot button (

) to plot the function using the given argument range. You can also click the
Create Plot button (

) in order to create a plot group, under the
Results node.