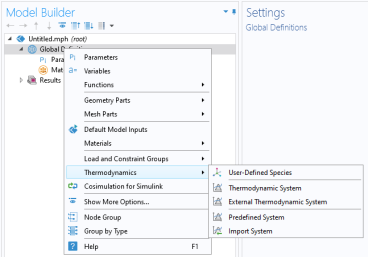
To access the functionality for thermodynamic calculations, right-click the Global Definitions node in the
Model Builder tree and select
Thermodynamics (

). When the model includes a Component,
Thermodynamics is also available on the
Physics toolbar.
Select Thermodynamic System in the context menu to add a thermodynamic system that uses the built-in database included with COMSOL Multiphysics.
As an alternative, selecting External Thermodynamic System can make use of an installed thermodynamics software to make the corresponding calculations.
The option Predefined System, allows you to set up one of the following systems; Dry air, Moist air, or Water-steam.
In addition to creating thermodynamic systems, you can also define User-Defined Species in Thermodynamics. Use
User-Defined Species to add new species that are not available in the COMSOL database. You can also edit available species in the database.