The Turbulent Flow, SST (spf) interface (

) is used for simulating single-phase flows at high Reynolds numbers. The physics interface is suitable for incompressible flows, weakly compressible flows, and compressible flows at low Mach numbers (typically less than 0.3).
When this physics interface is added, the following default nodes are also added in the Model Builder:
Fluid Properties,
Wall (the default boundary condition is
No slip), and
Initial Values.
A different turbulence model can be selected under Turbulence model. Laminar or creeping flow may simulated by changing the
Turbulence model type to
None.
The Turbulence model property disables the
Neglect inertial term (Stokes flow) check box, and for 2D components also the
Shallow Channel Approximation check box.
The SST model employs per default an Automatic wall treatment, which switches between a low-Reynolds-number formulation and a wall function formulation depending on how well resolved the flow is close to the wall. The automatic wall treatment gives a robust formulation that makes the most out of the available resolution.
Select the Low Re option in order to enforce resolution all the way down to the wall. This can be more accurate than the automatic wall treatment provided that the mesh is fine enough.
Turbulence model parameters are optimized to fit as many flow types as possible, but for some special cases, better performance can be obtained by tuning the model parameters. For this physics interface the turbulence model parameters are a1,
β0∗,
β1 ,β2 ,γ1 ,γ2, σk1,
σk2,
σw1, and
σw2, and the transition model parameters (when
Include transition modeling is enabled) are
ce2,
ca2,
σγ,
CTU1,
CTU2,
CTU3,
CPG1,
CPG2,
CPG3,
 ,
, 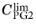
,
Ck,
CSEP,
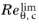
.
The SST interface requires a
Wall Distance Initialization study step in the study previous to the Stationary or Time Dependent study step.