The Shallow Water Equations, Time Explicit (swe) interface (
), found under the
Shallow Water Equations branch (
) when adding a physics interface, is used to solve the Shallow Water equations in a 1D or 2D geometry. These equations model the flow of a free surface in a fluid under the assumption that the horizontal scale is much greater than the vertical length scale. They are frequently used for modeling both oceanographic and atmospheric fluid flow. Models of such systems can be used to predict areas affected by pollution, coastal erosion, and polar ice-cap melting, provided the fluid layer is shallow enough.
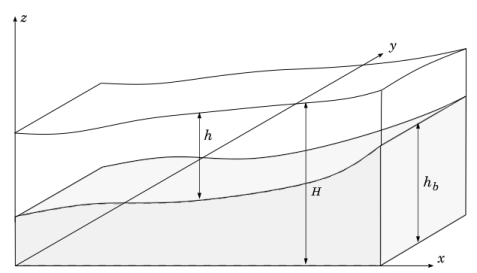
A typical configuration for the flow of fluid in a shallow layer is shown in Figure 10-1.This physics interface approximates free surface problems where the thickness
h of the fluid layer, or water depth, is small compared to the lateral dimensions of the geometry. The lower boundary of the fluid is treated as a nonpenetrable wall and has a height
hb(x, y) over a reference
xy-plane placed at
z = 0. The topography of the bottom is assumed constant in time. Using the shallow water equations, the water depth
h and water flux
q are computed in a reduced dimension of the problem. Free surface problems that would require a 3D geometry when modeled with the Navier–Stokes equations can be modeled in 2D instead. 2D problems can also be reduced to 1D.
When this physics interface is added, the following default nodes are also added in the Model Builder —
Domain Properties,
Wall, and
Initial Values. Then, from the
Physics toolbar, you can add other nodes that implement, for example, boundary conditions. You can also right-click
Shallow Water Equations, Time Explicit to select physics features from the context menu.
The Label is the default physics interface name.
The Name is used primarily as a scope prefix for variables defined by the physics interface. Refer to such physics interface variables in expressions using the pattern
<name>.<variable_name>. In order to distinguish between variables belonging to different physics interfaces, the
name string must be unique. Only letters, numbers, and underscores (_) are permitted in the
Name field. The first character must be a letter.
The default Name (for the first physics interface in the model) is
swe.
Select a value for Acceleration of gravity (SI unit m/s). The default value is
gconst. It should be a global quantity.
To display this section, click the Show More Options button (

) and select
Advanced Physics Options in the
Show More Options dialog box. Normally these settings do not need to be changed.
Select the CFL number. This CFL number will be used when defining the
Cell time scale expression swe.wtc used in the
Time-Explicit Solver if the
Time stepping is set to
From expressions. Note that the method will be unstable for CFL numbers larger than
1.
The dependent variables (field variables) are the Water depth h (SI unit: m) and the
Water flux q (SI unit: m
2 /s). The names can be changed but the names of fields and dependent variables must be unique within a component.
