The Wall node includes a set of boundary conditions to describe the flow conditions at a solid wall. The conditions for each phase are selected separately.
A No slip condition models a wall where the velocity of the continuous phase relative to the wall velocity is zero. For a stationary wall, it sets the velocity of the continuous phase to zero:
The Slip option prescribes a no-penetration condition. For a stationary wall,
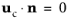
. It is implicitly assumed that there are no viscous effects at the slip wall and hence, no boundary layer develops.
Select the Leakage check box to specify an
Inward continuous phase mass flux,
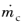
(SI unit: kg
/(m
2·s)). This option is intended for small values of
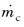
. For large mass fluxes, select us an Inlet feature instead.
Select a Dispersed velocity boundary condition —
No slip (the default), or
Slip. The conditions prescribed for the velocity of the dispersed phase correspond to those described for the continuous phase above.
The Dispersed Phase Boundary Condition defines the condition at the wall for the volume fraction of the dispersed phase.
The Translational velocity setting controls the translational wall velocity,
utr. The list is per default set to
Automatic from frame. The physics automatically detects if the spatial frame moves. This can for example happen if an ALE interface is present in the model component. If there is no movement
utr = 0. If the frame moves,
utr becomes equal to the frame movement.
utr is accounted for in the actual boundary condition prescribed in the
Boundary condition section.
Select Manual from
Translational velocity selection list in order to manually prescribe
Velocity of moving wall,
utr. This can for example be used to model an oscillating wall where the magnitude of the oscillations are very small compared to the rest of the model. Specifying translational velocity manually does not automatically cause the associated wall to move. An additional Moving Mesh interface needs to be added to physically track the wall movement in the spatial reference frame.
The Sliding wall option is appropriate if the wall behaves like a conveyor belt; that is, the surface is sliding in its tangential direction. A velocity is prescribed at the wall and the boundary itself does not have to actually move relative to the reference frame.