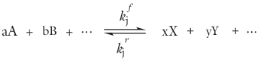
For laminar flow, or when the Turbulent-reaction model is set to
None in a
Reaction feature (in Transport of Concentrated Species), the default (Automatic) reaction rate used by the
Reaction feature is based on the mass action law. Consider a general reaction belonging to a set of
j reactions and involving
i species:
For such a reaction set, the reaction rates rj (SI unit: mol/(m
3·s)), can be described by the mass action law:
Here, 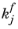 and
and 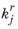 denote the forward and reverse rate constants, respectively. The concentration of species i
denote the forward and reverse rate constants, respectively. The concentration of species i is denoted
ci (SI unit: mol/m
3). The stoichiometric coefficients are denoted
νij, and are defined to be negative for reactants and positive for products. In practice, a reaction seldom involves more than two species colliding in a reacting step, which means that a kinetic expression is usually of order 2 or less (with respect to the involved concentrations).
Here, A denotes the frequency factor,
n the temperature exponent,
E the activation energy (SI unit: J/mol) and
Rg the gas constant,
8.314 J/(mol·K). The pre-exponential factor, including the frequency factor
A and the temperature factor
Tn, is given the units (m
3/mol)
α − 1/s, where
α is the order of the reaction (with respect to the concentrations).