Use the High Mach Number Reacting Flow (

) multiphysics coupling to simulate mass transport and reactions in a gas mixture where the fluid flow can be dependent on the mixture composition.
Select a Fluid Flow interface and a
Species transport interface to couple fluid flow with mass transport.
Chemistry is optional, and if it is selected, the fluid properties are taken from the
Chemistry interface.
The High Mach Number Reacting Flow coupling synchronizes the features from a High Mach Number Flow interface, a Transport of Concentrated Species interface and, optionally, a Chemistry interface. When the Chemistry interface is not selected, the density in the High Mach Number Flow interface is automatically synchronized to the one defined by the Transport of Concentrated Species interface.
When a Chemistry interface is selected, the High Mach Number Reacting Flow coupling synchronizes the definition of the thermal conductivity, density, heat capacity, enthalpy, molar mass and dynamic viscosity with the other coupled physics interfaces. The reference temperature is taken from the High Mach Number Flow interface.
The High Mach Number Reacting Flow coupling feature automatically couples mass transfer on boundaries and applies a corresponding velocity contribution for the flow. Prescribing a net mass boundary flux in the
Transport of Concentrated Species interface, either using a
Flux or
Mass Fraction feature, the
High Mach Number Reacting Flow feature computes
The Stefan Velocity and applies this in
Wall features using the same selection.
When a turbulence model is used, the High Mach Number Reacting Flow coupling applies turbulence modeling for the mass transport in the following manners:
The Label is the default multiphysics coupling feature name.
The Name is used primarily as a scope prefix for variables defined by the coupling node. Refer to such variables in expressions using the pattern
<name>.<variable_name>. In order to distinguish between variables belonging to different coupling nodes or physics interfaces, the
name string must be unique. Only letters, numbers, and underscores (_) are permitted in the
Name field. The first character must be a letter.
The default Name (for the first multiphysics coupling feature in the model) is
hmnrf1.
The High Mach Number Reacting Flow coupling is automatically defined on the intersection of the selections for the coupled interfaces.
The Selection list displays the domains where the coupling feature is active.
This section defines the physics involved in the multiphysics coupling. The Fluid flow, Species transport, and
Chemistry lists include all applicable physics interfaces.
You can also select None from a list to uncouple the node from a physics interface.
Click the Go to Source buttons (
) to move to the main physics interface node for the selected physics interface.
Click the Show or Hide Physics Properties Settings button (

) to toggle the display of physics properties settings affecting the coupling feature. When a turbulence model is used, turbulent mass transfer is automatically accounted for (see the settings in the
Turbulence section below). Using
High Mach Number Reacting Flow coupling, the mass transfer treatment at walls follows that applied for the fluid flow. Therefore the
Wall treatment setting is also displayed when using a turbulence model. For more information on turbulent mass transfer at walls, see the section
Mass Transport Wall Functions in the
CFD Module User’s Guide.
The turbulent mass transfer added to the mass fraction equations is defined as, 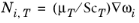 , where, μT
, where, μT is the turbulent viscosity defined by the flow interface, and the turbulent Schmidt number,
ScT, depends on the
Mass transport turbulence model used.
The Turbulence model type used by the fluid flow interface can be displayed by selecting the
Show or Hide Physics Property Settings button at the right of the
Fluid flow list.