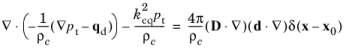
|
•
|
Free space reference power (RMS), Prms (SI unit: W). In a homogeneous medium, the specified power is radiated (the reference), but with other objects and boundaries present the actual power is different.
|
|
•
|
|
•
|
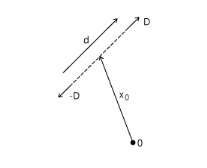
Quadrupole direction,
 |
|
•
|
Free space reference power (RMS), Prms (SI unit: W). In a homogeneous medium, the specified power is radiated (the reference), but with other objects and boundaries present the actual power is different.
|
|
•
|
|
•
|
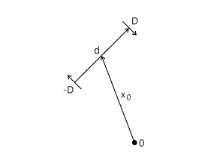
Quadrupole normal, n (dimensionless). This is the normal to the plane in which the quadrupole is located.
|
|
•
|
Quadrupole direction,
 |