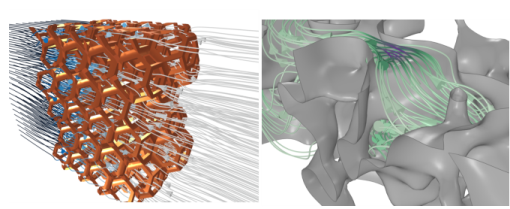
If it is possible to calculate averaged values from the simulation on a microscopic scale (Figure 2-1), which are also representative for any other section, the modeled section is called a representative elementary volume (REV). Two variables mainly characterize the porous material: The porosity describes the ratio of void/pore volume to total volume
and the permeability κ(m
2) specifies the ability of a fluid to pass through it.