
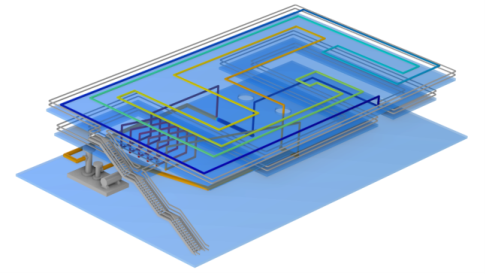
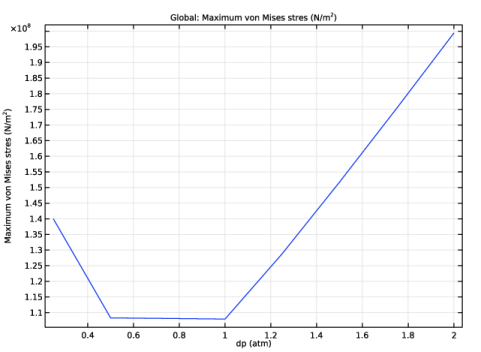
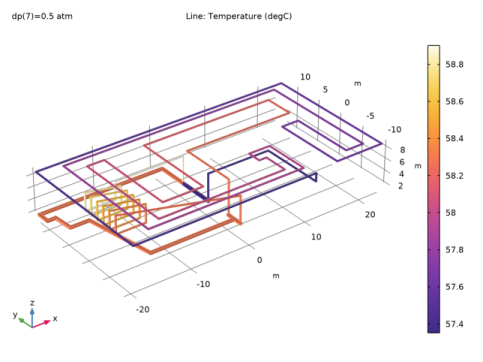
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
In the Select Physics tree, select Structural Mechanics>Fluid-Structure Interaction>Fluid-Pipe Interaction, Fixed Geometry.
|
|
3
|
Click Add.
|
|
4
|
Click
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Click
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
Browse to the model’s Application Libraries folder and double-click the file cooling_pipeline_stress_main.txt.
|
|
5
|
Locate the Selections of Resulting Entities section. Select the Resulting objects selection check box.
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
Click OK.
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
Browse to the model’s Application Libraries folder and double-click the file cooling_pipeline_stress_inlet.txt.
|
|
5
|
Locate the Selections of Resulting Entities section. Select the Resulting objects selection check box.
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
Click OK.
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
Browse to the model’s Application Libraries folder and double-click the file cooling_pipeline_stress_outlet.txt.
|
|
5
|
Locate the Selections of Resulting Entities section. Select the Resulting objects selection check box.
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
Click OK.
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
Browse to the model’s Application Libraries folder and double-click the file cooling_pipeline_stress_heater.txt.
|
|
5
|
Locate the Selections of Resulting Entities section. Select the Resulting objects selection check box.
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
Click OK.
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
Click OK.
|
|
6
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
Click OK.
|
|
6
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
In the Paste Selection dialog box, type pare2(1): 12, 16, 23, 29 pol2: 3, 4 pol4: 3 in the Selection text field.
|
|
5
|
Click OK.
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
On the object pare3(3), select Point 2 only.
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
On the object pare3(3), select Point 25 only.
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
|
10
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
In the tree, select Built-in>Air.
|
|
6
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
From the list, choose Circular.
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
Locate the Flow Resistance section. From the Surface roughness list, choose Commercial steel (0.046 mm).
|
|
1
|
In the Model Builder window, under Component 1 (comp1)>Pipe Mechanics (pipem) click Fluid and Pipe Materials 1.
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
From the list, choose Circular.
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
In the Paste Selection dialog box, type 1-3, 7, 10-22, 25, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34-46, 48, 57, 59-61, 63-67, 69, 70, 77-80, 82-86, 90-96, 100, 101, 105 in the Selection text field.
|
|
5
|
Click OK.
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
In the Paste Selection dialog box, type 2-7, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22-34, 36, 38, 40, 42, 44, 46-49, 51-60, 63-65, 67, 68, 70-84, 86-105 in the Selection text field.
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
In the Settings window for Prescribed Displacement/Rotation, locate the Prescribed Displacement section.
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
In the Settings window for Prescribed Displacement/Rotation, locate the Prescribed Displacement section.
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
In the Settings window for Prescribed Displacement/Rotation, locate the Coordinate System Selection section.
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
Locate the Prescribed Displacement section. From the Prescribed in x2 direction list, choose Limited.
|
|
9
|
|
10
|
|
11
|
|
12
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
In the Model Builder window, under Component 1 (comp1)>Heat Transfer in Pipes (htp) click Heat Transfer 1.
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
From the list, choose Circular.
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
Locate the Flow Resistance section. From the Surface roughness list, choose Commercial steel (0.046 mm).
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
Click OK.
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
In the Paste Selection dialog box, type 4-9, 30-34, 39-43, 51-54, 56, 59-64, 69, 73, 76-87, 90-106 in the Selection text field.
|
|
5
|
Click OK.
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
Right-click Study 1>Solver Configurations>Solution 1 (sol1)>Dependent Variables 1 and choose Update Variables.
|
|
3
|
In the Model Builder window, expand the Study 1>Solver Configurations>Solution 1 (sol1)>Stationary Solver 1 node.
|
|
4
|
In the Model Builder window, expand the Study 1>Solver Configurations>Solution 1 (sol1)>Stationary Solver 1>Segregated 1 node, then click Segregated Step 1.
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Click to expand the Method and Termination section. From the Nonlinear method list, choose Automatic (Newton).
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
Right-click Study 1>Solver Configurations>Solution 1 (sol1)>Stationary Solver 1>Segregated 1>Heat and choose Move Up.
|
|
10
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
Select the Plot check box.
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Click
|
|
8
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
6
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
8
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
In the Model Builder window, expand the Results>Section Forces (pipem) node, then click Total Bending Moment (pipem).
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
5
|