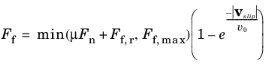The Friction (Rigid Body Contact) feature is used to add frictional forces and losses to the
Rigid Body Contact.
Here, Fn is the contact force,
Ff,r is the additional sliding resistance,
Ff,max is the maximum friction force,
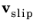
is the slip velocity vector and
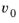
is the characteristic slip velocity.
where vc,s and
vc,d are the velocities of the source and destination spheres at the contact point. They are defined as
where vsrc and
vdst are the velocity vectors of the centers of the source and destination spheres, and the angular velocity vectors of the source and destination spheres are given by
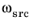
and
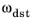
. The distance vectors from the centers of the source and destination, to the contact point, are given by
rs and
rd. They are defined as
where rs and
rd are the radii of the source and destination spheres.
where Ff is the magnitude of the friction force. The friction force vector is applied also on the destination sphere, but with opposite sign.
where qsrc and
qdst are the quaternions of the source and destination spheres.
Friction is formulated in the same way in the Spherical to Cylindrical Formulation, the
Spherical to Planar Formulation, the
Cylindrical to Cylindrical Formulation and the
Cylindrical to Planar Formulation. The only difference is the computation of the distance vectors from the source and destination centers to the contact point, denoted by
rs and
rd. In each case, based on the source and destination geometries, they are calculated from the undeformed locations of the source and destination centers and direction vector from the source contact point to the destination contact point.
where vc,s is the velocity of the source sphere at the contact point. It is defined as
where vsrc is the velocity vector of the source center and
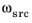
is the angular velocity vector of the source sphere. The distance vector from the center to the contact point for the source is defined as
where rs is the radius of the source sphere. The velocity of the destination boundary, at the contact point, is
vc,d.
where Ff is the magnitude of the friction force. The friction force vector applied on the destination sphere has equal magnitude, but points in the opposite direction.
where qsrc is the quaternion of source sphere.