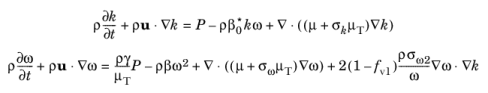To combine the superior behavior of the k-
ω model in the near-wall region with the robustness of the
k-
ε model, Menter (
Ref. 18) introduced the SST (Shear Stress Transport) model which interpolates between the two. The version of the SST model in the CFD Module includes a few well-tested (
Ref. 17,
Ref. 19) modifications, such as production limiters for both
k and
ω, the use of
S instead of
Ω in the limiter for
μT and a sharper cutoff for the cross-diffusion term.
and Pk is given in
Equation 3-78. The turbulent viscosity is given by,
where S is the characteristic magnitude of the mean velocity gradients,
where lw is the distance to the closest wall.
Realizability Constraints are applied to the SST model.
The wall distance variable, lw, is provided by a mathematical Wall Distance interface that is included when using the SST model. The solution to the wall distance equation is controlled using the parameter
lref. The distance to objects larger than
lref is represented accurately, while objects smaller than
lref are effectively diminished by appearing to be farther away than they actually are. This is a desirable feature in turbulence modeling since small objects would get too large an impact on the solution if the wall distance were measured exactly.
When Wall Treatment is set to
Automatic the same type of formulation described for the
k-
ω model is applied at the boundary but with
β1 instead of
β0. See
Automatic Wall Treatment for more details.
To avoid the singularity at the wall, ω is not solved for in the cells adjacent to a solid wall. Instead, its value is prescribed by
Equation 3-108 (using the variable
ωw, which only exists in those cells). Accurate solutions in the near-wall region require that,
where uτ is the friction velocity which is calculated from the wall shear-stress
τw,
The boundary variable Distance to cell center in viscous units,
lplus_cc, is available to ensure that the mesh is fine enough. According to
Equation 3-109,
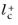
should be about
0.5. Observe that very small values of
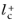
can reduce the convergence rate.
The guidelines given in Inlet Values for the Turbulence Length Scale and Turbulent Intensity for selecting the turbulence length scale,
LT, and the turbulence intensity,
IT, apply also to the SST model.
where L is the approximate length of the computational domain.