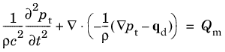The Transient Pressure Acoustics Model node adds the equations for primarily time-dependent (transient) acoustics modeling. This is the scalar wave equation
where pt is the total acoustic pressure,
ρ is the fluid density,
c is the speed of sound,
qd is the
Dipole Domain Source, and
Qm is the
Monopole Domain Source. In this formulation of the wave equation, the speed of sound and density may in general be space dependent but only slowly varying in time, that is, at a time scale much slower than the variations in the acoustic signal.
In the Settings window, define the properties for the acoustics model and model inputs including temperature.
Select a Fluid model:
Linear elastic (the default),
Viscous,
Thermally conducting,
Thermally conducting or viscous,
General dissipation, or
Ideal Gas. Then see the descriptions for
The Pressure Acoustics, Frequency Domain Interface:
When Ideal gas is selected as the
Fluid model, both the
Temperature T and
Absolute pressure pA fields are always enabled. Select,
User defined (the default),
Common model input, or an input from another physics interface, if applicable.
In addition, the Temperature T and
Absolute pressure pA can be picked up from another physics interface where the fields have been calculated. For example, select a temperature field defined by a
Heat Transfer interface or a
Nonisothermal Flow interface (if any). Or, if applicable, select a pressure as defined by a
Fluid Flow interface present in the model. For example, select
Absolute pressure (spf) to use the absolute pressure defined by a
Laminar Flow interface
spf.