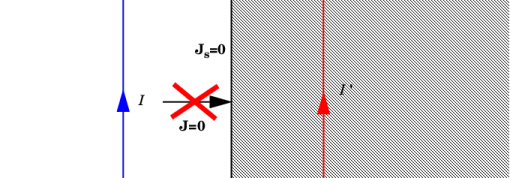
The Perfect Magnetic Conductor boundary condition
n × H = 0 is a special case of the surface current boundary condition that sets the tangential component of the magnetic field and thus also the surface current density to zero. On external boundaries, this can be interpreted as a “high surface impedance” boundary condition or used as a symmetry type boundary condition. It imposes symmetry for electric fields and electric currents. Electric currents (volume, surface, or edge currents) are not allowed to flow into a perfect magnetic conductor boundary as that would violate current conservation. On interior boundaries, the perfect magnetic conductor boundary condition literally sets the tangential magnetic field to zero, which, in addition to setting the surface current density to zero, also makes the tangential magnetic vector potential (and in dynamics the tangential electric field) discontinuous.