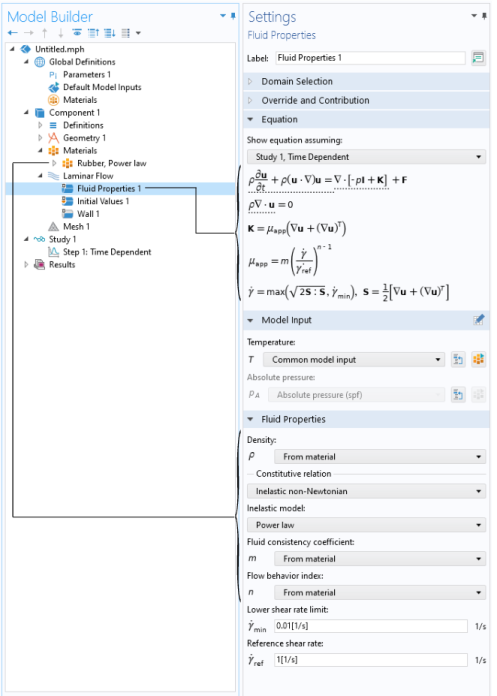
Figure 4 shows the Model Builder, including a Laminar Flow interface, and the Settings window for the selected Fluid Properties 1 feature node. The Fluid Properties 1 node adds the marked terms to the component equations in a selected geometry domain. Furthermore, the Fluid Properties 1 feature may link to the Materials feature node to obtain physical properties such as density and constitutive parameters, in this case rubber modeled with a power-law fluid. The fluid properties, defined by the Rubber, Power law material, can be functions of the modeled physical quantities, such as pressure and temperature. In the same way, the Wall 1 node adds the boundary conditions at the walls of the fluid domain.
Figure 5 shows the Polymer Flow Module interfaces as they are displayed when you add a physics interface (see also
Physics Interface Guide by Space Dimension and Study Type for further information). A short description of the physics interfaces follows.