
|
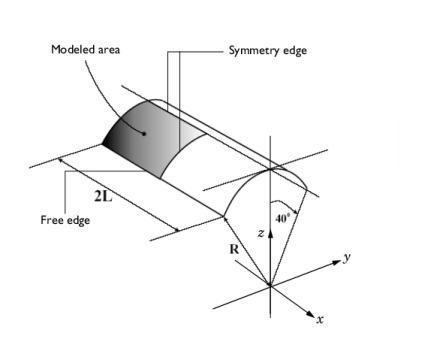
|
•
|
|
•
|
|
•
|
|
•
|
|
•
|
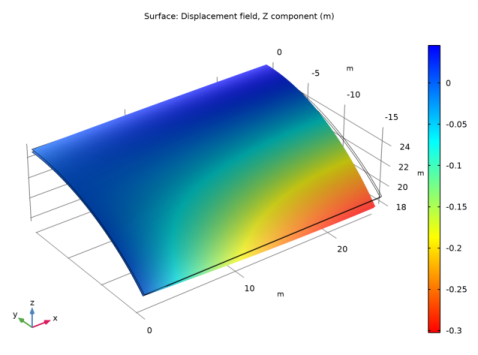
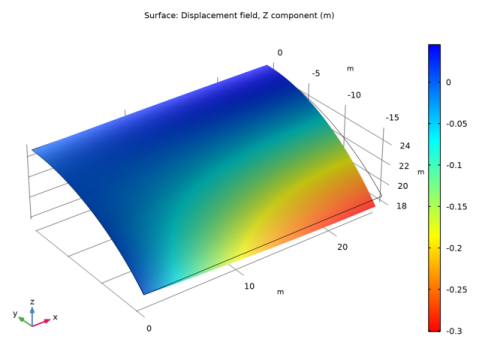
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
Click Add.
|
|
4
|
Click
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Click
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
In the Model Builder window, under Component 1 (comp1)>Geometry 1 right-click Work Plane 1 (wp1) and choose Revolve.
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
Click the Angles button.
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Locate the Revolution Axis section. Find the Direction of revolution axis subsection. In the xw text field, type 1.
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
3
|
In the Settings window for Prescribed Displacement/Rotation, locate the Prescribed Displacement section.
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
In the Model Builder window, under Component 1 (comp1) right-click Materials and choose Blank Material.
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
In the Settings window for Surface, click Replace Expression in the upper-right corner of the Expression section. From the menu, choose Component 1 (comp1)>Shell>Displacement>Displacement field - m>w - Displacement field, Z component.
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
In the Model Builder window, expand the Results>Datasets node, then click Study 1: Tri Normal/Solution 1 (sol1).
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
In the Model Builder window, under Results>Datasets click Study 3: Quad Extra fine/Solution 3 (sol3).
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
In the Model Builder window, under Results>Datasets click Study 4: Tri Extra fine/Solution 4 (sol4).
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
3
|
|
5
|
Click
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
Locate the Expressions section. In the table, enter the following settings:
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
Locate the Expressions section. In the table, enter the following settings:
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
Locate the Expressions section. In the table, enter the following settings:
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
Locate the Expressions section. In the table, enter the following settings:
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
Locate the Expressions section. In the table, enter the following settings:
|
|
5
|