
|
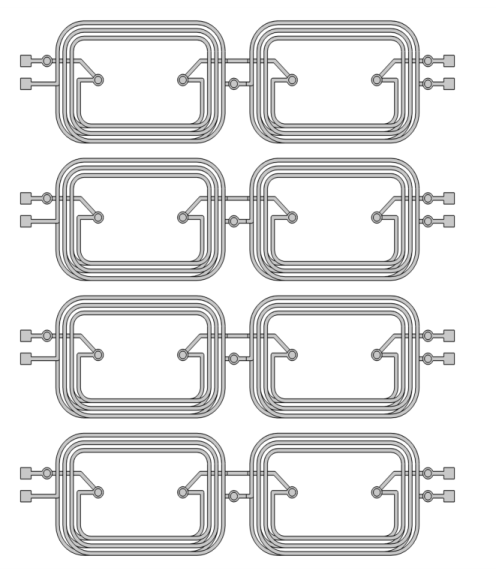
|
1
|
|
2
|
In the Select Physics tree, select AC/DC>Electromagnetic Fields>Vector Formulations>Magnetic Fields, Currents Only (mfco).
|
|
3
|
Click Add.
|
|
4
|
Click
|
|
5
|
In the Select Study tree, select Preset Studies for Selected Physics Interfaces>Stationary Source Sweep with Initialization.
|
|
6
|
Click
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
Click Import.
|
|
6
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
On the object imp1, select Domains 4, 5, 8–15, 26–31, and 34–54 only.
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
Click
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
Click OK.
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
On the object imp1, select Domains 1–3, 6, 7, 16–25, 32, and 33 only.
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
Select the object del1 only.
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
Select the object dif1 only.
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
Select the objects spl1(15), spl1(16), spl1(17), spl1(18), spl1(19), spl1(20), spl1(21), spl1(22), spl1(23), spl1(24), spl1(25), spl1(26), spl1(27), spl1(28), spl1(29), spl1(30), spl1(31), spl1(32), spl1(33), spl1(34), spl1(35), spl1(50), spl1(51), spl1(52), spl1(53), spl1(54), spl1(55), spl1(56), spl1(57), and spl1(59) only.
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
On the object mov1(26), select Boundary 1 only.
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
Select the objects spl1(1), spl1(10), spl1(11), spl1(12), spl1(13), spl1(14), spl1(2), spl1(3), spl1(4), spl1(5), spl1(6), spl1(60), spl1(7), spl1(8), and spl1(9) only.
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
Select the objects ext1, mov1(22), mov1(23), mov1(25), mov1(27), mov1(28), mov1(29), spl1(36), spl1(37), spl1(38), spl1(39), spl1(40), spl1(41), spl1(42), spl1(43), spl1(44), spl1(45), spl1(46), spl1(47), spl1(48), spl1(49), and spl1(58) only.
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
Select the objects mov1(1), mov1(10), mov1(11), mov1(12), mov1(13), mov1(14), mov1(15), mov1(16), mov1(17), mov1(18), mov1(19), mov1(2), mov1(20), mov1(21), mov1(24), mov1(3), mov1(30), mov1(4), mov1(5), mov1(6), mov1(7), mov1(8), and mov1(9) only.
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
Click in the Graphics window and then press Ctrl+A to select all objects.
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
Click in the Graphics window and then press Ctrl+A to select all objects.
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
Locate the Selections of Resulting Entities section. Select the Resulting objects selection check box.
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
Select the object blk3 only.
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
Select the object par1 only.
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
Select the object par2 only.
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
Click OK.
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
|
10
|
|
11
|
|
12
|
|
13
|
|
14
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Click OK.
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
|
10
|
|
11
|
|
12
|
|
13
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Click OK.
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
|
10
|
|
11
|
|
12
|
|
13
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Click OK.
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
|
10
|
|
11
|
|
12
|
|
13
|
|
14
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Click OK.
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
|
10
|
|
11
|
|
12
|
|
13
|
|
14
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Click OK.
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
|
10
|
|
11
|
|
12
|
|
13
|
|
14
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Click OK.
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
|
10
|
|
11
|
|
12
|
|
13
|
|
14
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Click OK.
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
|
10
|
|
11
|
|
12
|
|
13
|
|
14
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Click OK.
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
|
10
|
|
11
|
|
12
|
|
13
|
|
14
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Click OK.
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
|
10
|
|
11
|
|
12
|
|
13
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Click OK.
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
|
10
|
|
11
|
|
12
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
Click OK.
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
|
10
|
|
11
|
|
12
|
|
13
|
|
1
|
In the Model Builder window, under Component 1 (comp1) right-click Magnetic Fields, Currents Only (mfco) and choose Conductor.
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
1
|
In the Model Builder window, under Component 1 (comp1) right-click Materials and choose Blank Material.
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
|
8
|
|
9
|
|
10
|
|
11
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
1
|
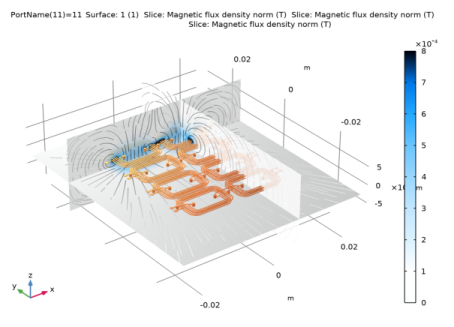
In the Model Builder window, expand the Results>Derived Values node, then click Inductance (mfco, dset1).
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
Click
|
|
1
|
Go to the Table window.
|
|
2
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|
|
4
|
|
5
|
|
6
|
|
7
|
|
1
|
|
2
|
|
3
|