where h=hw+hb and the tangential velocity,
vav represents the mean velocity of the flow in the reference plane. Particular care must be taken with respect to the definition of
h. The above equation applies if
h is measured with respect to a fixed point on the reference surface as a function of time. The reference surface itself must be fixed in space and obviously cannot deform as time progresses. Equations represented on the reference surface are described as Eulerian, that is they are defined in a frame that is fixed with respect to the motion of the fluid or of the body. Fluid flow problems are usually formulated in the Eulerian frame, and COMSOL Multiphysics adopts this convention in most of its fluid flow interfaces. It is useful to note that the Eulerian frame is usually called the spatial frame within the COMSOL Multiphysics interface. When a structure deforms in COMSOL Multiphysics, the spatial frame changes shape.
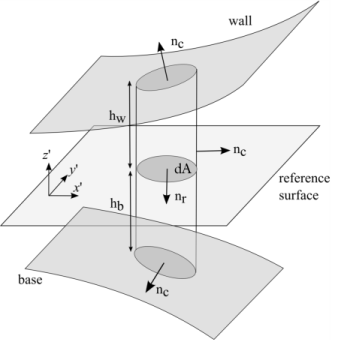
The situation encountered when both the wall and the base undergo a displacement is depicted in Figure 4-4. The Eulerian wall height changes from an initial value
hw1 to a final value
hw. Similarly the base height changes from an initial value
hb1 to
hb.
The definition of the average flow velocity, vav, together with the forces that act on the structure, remain to be specified.