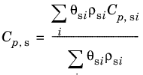This node defines the porosity and material properties of the solid matrix used in Equation 6-6 or
Equation 6-13 of the
Moist Porous Medium and
Porous Medium parent nodes, to model heat transfer in a porous matrix, possibly consisting of several solids, and filled with a mobile fluid, and one or more immobile fluids.
This section is available when a temperature-dependent density defined in a material is used. On the material frame, the density is evaluated in relation to a reference temperature in order to ensure conservation of the mass in the presence of temperature variations. By default the Common model input is used. This corresponds to the variable
minput.Tempref, which is set to 293.15 K by default. To edit it, click the
Go to Source button (

), and in the
Default Model Inputs node under
Global Definitions, set a value for the
Volume reference temperature in the
Expression for remaining selection section.
Other options are User defined and all the temperature variables from the physics interfaces included in the model.
This section is available when material properties are temperature-dependent. By default, the temperature of the parent interface is used and the section is not editable. To edit the Temperature field, click
Make All Model Inputs Editable (

). The available options are
User defined (default),
Common model input (the
minput.T variable, set to 293.15 K by default) and all temperature variables from the physics interfaces included in the model. To edit the
minput.T variable, click the
Go to Source button (

), and in the
Default Model Inputs node under
Global Definitions, set a value for the
Temperature in the
Expression for remaining selection section.
The default Porosity εp of the solid matrix is taken
From material. In a
Porous Material node, the porosity is defined as follows:
where θsi and
θimfi are the porosities of the
Solid and
Immobile Fluids subnodes under the
Porous Material node.
For User defined, enter a value or expression.
Choose to define either the Dry bulk properties or the
Solid phase properties for thermal conductivity, density, and heat capacity at constant pressure of the porous matrix. The first option sets the properties of the matrix including empty pores, while the second option defines the properties of the pure solid phase.
The thermal conductivity ks describes the relationship between the heat flux vector
q and the temperature gradient
∇T in
q = −ks∇T, which is Fourier’s law of heat conduction. Enter this quantity as power per length and temperature.
The default Thermal conductivity ks is taken
From material. For
User defined select
Isotropic,
Diagonal,
Symmetric, or
Full, based on the characteristics of the thermal conductivity, and enter another value or expression. For
Isotropic, enter a scalar which will be used to define a diagonal tensor. For the other options, enter values or expressions into the editable fields of the tensor.
When the thermal conductivity is taken From material and more than one
Solid subnode is added under the
Porous Material node, the average property is obtained by applying a volume average model:
Alternatively, set the Dry bulk thermal conductivity kb, when
Define is set to
Dry bulk properties in the
Matrix Properties section. The corresponding property for the solid phase is then defined as:
The Density ρs and the
Specific heat capacity Cp, s should be specified. For
From Material option, see
Material Density in Features Defined in the Material Frame if a temperature-dependent density should be set.
When the density and specific heat capacity are taken From material and more than one
Solid subnode is added under the
Porous Material node, the effective properties are obtained by applying a volume averaging model:
Alternatively, set the Dry bulk density ρb and the
Dry bulk heat capacity at constant pressure Cp,b when
Define is set to
Dry bulk properties in the
Matrix Properties section. The corresponding properties for the solid phase are then defined as:
Physics Tab with Porous Medium or
Moist Porous Medium selected in the model tree: