The Free and Porous Media Flow (fp) interface (

), found under the
Porous Media and Subsurface Flow branch (

) when adding a physics interface, is used to compute fluid velocity and pressure fields of single-phase flow where free flow is connected to porous media. The Free and Porous Media Flow interface is used over at least two different domains: a free channel and a porous medium. The physics interface is well suited for transitions between slow flow in porous media, governed by the Brinkman equations, and fast flow in channels described by the Navier–Stokes equations. Fluids with varying density can be included at Mach numbers below 0.3. Also the viscosity of a fluid can vary, for example, to describe non-Newtonian fluids. The physics interface can be used for stationary and time-dependent analyses.
When this physics interface is added, the following default nodes are also added in the Model Builder —
Fluid Properties,
Wall, and
Initial Values. Then, from the
Physics toolbar, add a
Fluid and Matrix Properties node to be used on the domain selection corresponding to the porous media, or add other nodes that implement, for example, boundary conditions and volume forces. You can also right-click
Free and Porous Media Flow to select physics features from the context menu.
The Label is the default physics interface name.
The Name is used primarily as a scope prefix for variables defined by the physics interface. Refer to such physics interface variables in expressions using the pattern
<name>.<variable_name>. In order to distinguish between variables belonging to different physics interfaces, the
name string must be unique. Only letters, numbers, and underscores (_) are permitted in the
Name field. The first character must be a letter.
The default Name (for the first physics interface in the model) is
fp.
By default the physics interface uses the Incompressible flow formulation of the Navier–Stokes and Brinkman equations to model constant density flow. If required, select
Compressible flow (Ma<0.3) from the
Compressibility list, to account for small variations in the density, typically dependent on the temperature (nonisothermal flow). For compressible flow modeled with this physics interface, the Mach number must be below 0.3.
Select the Neglect inertial term (Stokes flow) check box if the inertial forces are small compared to the viscous forces. This is typical for creeping flow, where
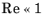
.
Enter a Reference pressure level pref (SI unit: Pa). The default value is
1[atm].
Enter a Reference temperature Tref (SI unit: K). The default value is
293.15[K].
For 2D axisymmetric components, select the Swirl flow check box to include the swirl velocity component, that is the velocity component
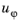
in the azimuthal direction. While
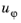
can be nonzero, there can be no gradients in the
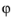
direction.