where σl denotes the electrolyte conductivity,
R the molar gas constant,
T the
temperature,
F Faraday’s constant, and
t+ the transport number.
Current conservation is described by  . Here Ql
. Here Ql denotes the sum of all current contributions.
Where D (SI unit: mol/(s /m
2)) is the binary diffusion coefficient into which the migration effects are incorporated, and
u (SI unit: m/s) is the volume averaged velocity.
where Rl is the a source term (SI unit: mol/s /m
3) resulting from the electrochemical reactions. This source term is according to the equation below:
where nm denotes the number of electrons involved in reaction (dimensionless),
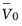
the partial molar volume of the solvent (H
2O
) (SI unit: m
3/mol),
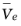
the partial molar volume of the electrolyte (SI unit: m
3/mol),
where 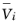 denotes the molar volumes (SI unit: m3
denotes the molar volumes (SI unit: m3/mol) for the solid materials in the electrodes,
the stoichiometric coefficient for lead sulfate in reaction m. For a species with a known density,
ρi (SI unit: kg/m
3), and molar mass
Mi it can be calculated as
Assuming that the main Pb and PbO2 reactions are the main contributions to the currents in each electrode, the average superficial velocity in each electrode compartment can be calculated as