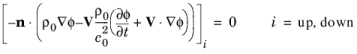For The Linearized Potential Flow, Frequency Domain Interface and
The Linearized Potential Flow, Transient Interface, use the
Interior Sound Hard Boundary (Wall) condition to model interior rigid boundary surfaces, or walls. It prescribes a vanishing normal component of the particle velocity at the boundary. Multiplied by the density, it can equivalently be expressed as a
no-flow condition: