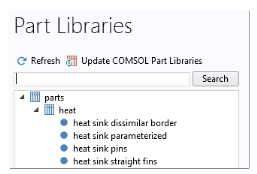
The library includes four parts. The Heat Sink — Parameterized Fin Types part is the most general part. It supports multiple parameterization, while a reduced number of parameters is available in the three other parts, as shown in
Table 3-13.
In the Heat Sink — Pin Fins part, all the fins are pins with the same dimension, whereas the outer and inner fins (in the
y direction) can have distinct dimensions in the
Heat Sink — Dissimilar Border Pins part. You may use the
Heat Sink — Straight Fins part to define a heat sink made of only straight fins.
By default, the base of the heat sink is positioned at the origin of the xy-plane. You can apply a
Displacement and a
Rotation to this configuration in the
Position and Orientation of Output section.