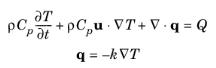
|
•
|
ρ (SI unit: kg/m3) is the fluid density.
|
|
•
|
Cp (SI unit: J/(kg·K)) is the fluid heat capacity at constant pressure.
|
|
•
|
k (SI unit: W/(m·K)) is the fluid thermal conductivity (a scalar or a tensor if the thermal conductivity is anisotropic).
|
|
•
|
u (SI unit: m/s) is the fluid velocity field, either an analytic expression or a velocity field from a Fluid Flow interface.
|
|
•
|
Q (SI unit: W/m3) is the heat source (or sink). Add one or several heat sources as separate physics features. See the Heat Source node and the Viscous Dissipation and Pressure Work subnodes, for example.
|
|
•
|
The gas constant, with two options for the Gas constant type: Specific gas constant Rs or Mean molar mass Mn. If Mean molar mass is selected the software uses the universal gas constant R = 8.314 J/(mol·K), which is a built-in physical constant, to compute the specific gas constant.
|
|
•
|
Either the Heat capacity at constant pressure Cp or Ratio of specific heats γ by selecting the option from the Specify Cp or γ list. For an ideal gas, it is sufficient to specify either Cp or the ratio of specific heats, γ, as these properties are interdependent.
|
|
•
|
Vapor mass fraction to define the ratio of the vapor mass to the total mass. Enter a value or expression for the Vapor mass fraction ω.
|
|
•
|
Concentration to define the amount of water vapor in the total volume. If selected, a Concentration model input is added in the Model Inputs section.
|
|
•
|
Moisture content (the default), also called mixing ratio or humidity ratio, to define the ratio of the water vapor mass to the dry air mass. For User defined, enter a value or expression for the Moisture Content xvap. Else, select an Ambient moisture content defined from an Ambient Properties node under Definitions.
|
|
•
|
Relative humidity
|
|
With certain COMSOL products, the Viscous Dissipation (for heat generated by viscous friction), Pressure Work, and Convectively Enhanced Conductivity subnodes are available from the context menu (right-click the parent node) or from the Physics toolbar, Attributes menu.
|
|
When Surface-to-surface radiation is activated, the Opacity (Surface-to-Surface Radiation Interface) subnode is automatically added to the entire selection, with Transparent option selected. The domain selection can’t be edited. To set some part of the domain as opaque, add a new Opacity (Surface-to-Surface Radiation Interface) subnode from the context menu (right-click the parent node) or from the Physics toolbar, Attributes menu.
|
|
Heat Sink: Application Library path Heat_Transfer_Module/Tutorials,_Forced_and_Natural_Convection/heat_sink
|