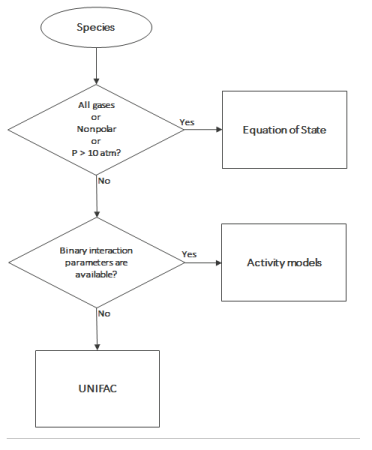
There are methods to choose the appropriate thermodynamic models; see Ref. 78. This choice depends on the nature of the property, composition of the mixture, operational pressure and temperature, and availability of model’s parameters for the simulation; see
Ref. 79. Below is a decision tree that can be used as a guide for choosing the thermodynamic model:
All the parameters and temperature-dependent properties are saved inside <Compound></Compound> command phrase. For example, to edit the acentric factor of methane from 0.01141 to 0.2, open the thermodynamic system file, and under compound methane, change the value for acentric factor as
<AcentricFactor >0.2</AcentricFactor>.
where Tlb and T
ub are lower and upper bound for temperature, respectively. The a
1 to a
4 are coefficients for a cubic polynomial as f(T) = a
0 + a
1*T+ a
2*T
2+ a
3*T
3 fitted to the experimental data. The unit for temperature is K; see
Table 6-3 for other units:
The database includes all the references for constant and temperature-dependent properties. In the saved thermodynamic system, it is located between <Comment></Comment>. Alternatively, under the
Thermodynamic System node, you can right-click on the created species function created and select
Properties.

