where μs is the solvent viscosity,
S is the strain-rate tensor, and
Te is the elastic stress tensor. To adequately describe a flow of fluid with a complex rheological behavior, symmetric stress tensor
Te is represented as a sum of the individual modes
where the relaxation function 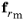
and the viscosity factor
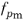
are model specific functions of stress,
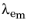
is a relaxation time,
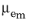
is a polymer viscosity, and the upper convective derivative operator is defined as
The first two terms on the left-hand side of Equation 4-29 represent the material derivative, and the other two terms represent the deformation. For more information, see
Ref. 7
where 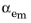
is the dimensionless mobility factor.