You are viewing the documentation for an older COMSOL version. The latest version is
available here.
The Wall node includes a set of boundary conditions describing fluid-flow conditions at stationary, moving, and leaking walls. For turbulent flow, the description may involve wall functions and asymptotic expressions for certain turbulence variables.
Select a Boundary condition for the wall.
No slip is the default boundary condition to model solid walls. A no slip wall is a wall where the fluid velocity relative to the wall velocity is zero. For a stationary wall that means that
u = 0.
When Wall Treatment is set to
Wall functions, the
Apply wall roughness option becomes available. When
Apply wall roughness is selected, a
Sand roughness model, derived from the experiments by Nikuradse, is applied. Select
Generic roughness in order to specify more general roughness types.
|
•
|
For Sand roughness an Equivalent sand roughness height kseq should be specified.
|
|
•
|
For Generic roughness a Roughness height ks and a dimensionless Roughness parameter Cs should be specified.
|
The Slip option prescribes a no-penetration condition,
u·
n=0. It is implicitly assumed that there are no viscous effects at the slip wall and hence, no boundary layer develops. From a modeling point of view, this can be a reasonable approximation if the main effect of the wall is to prevent fluid from leaving the domain.
When the Use viscous slip check box is selected, the default
Slip length Ls is
User defined. Another value or expression may be entered if the default value is not applicable. For
Maxwell’s model values or expressions for the
Tangential momentum accommodation coefficient av and the
Mean free path λ should be specified. Tangential accommodation coefficients are typically in the range of 0.85 to 1.0 and can be found in G. Kariadakis, A. Beskok, and N. Aluru,
Microflows and Nanoflows, Springer Science and Business Media, 2005.
When the Use thermal creep check box is selected, a thermal creep contribution with
Thermal slip coefficient σT is activated. Thermal slip coefficients are typically between 0.3 and 1.0 and can be found in G. Kariadakis, A. Beskok, and N. Aluru,
Microflows and Nanoflows, Springer Science and Business Media, 2005.
Slip velocity is available when
Turbulence Model in the
Turbulence section of the interface is set to
None.
where β is a slip length, and
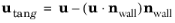
is the velocity tangential to the wall. The boundary condition does not set the tangential velocity component to zero; however, the extrapolated tangential velocity component is 0 at a distance
β outside of the wall.
The Slip Length setting is per default set to
Factor of minimum element length. The slip length
β is then defined as

, where
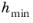
is the smallest element side (corresponds to the element size in the wall normal direction for boundary layer elements) and

is a user input. Select
User defined from
Slip Length selection list in order to manually prescribe
β (SI unit: m).
In cases where the wall movement is nonzero, check Account for the translational wall velocity in the friction force to use
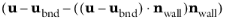
instead of
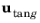
in the friction force. Then, the extrapolated tangential velocity component is
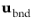
at a distance
β outside of the wall. Note that the
Velocity of sliding wall uw is always accounted for in the friction force.
Leaking Wall is available when Turbulence Model in the
Turbulence section of the interface is set to
None.
The Translational velocity setting controls the translational wall velocity,
utr. The list is per default set to
Automatic from frame. The physics automatically detects if the spatial frame moves. This can for example happen if an ALE interface is present in the model component. If there is no movement
utr = 0. If the frame moves,
utr becomes equal to the frame movement.
utr is accounted for in the actual boundary condition prescribed in the
Boundary condition section.
Select Zero (Fixed wall) from
Translational velocity selection list to prescribe
utr = 0.
Select Manual from
Translational velocity selection list in order to manually prescribe
Velocity of moving wall,
utr. This can for example be used to model an oscillating wall where the magnitude of the oscillations are very small compared to the rest of the model. Specifying translational velocity manually does not automatically cause the associated wall to move. An additional Moving Mesh interface needs to be added to physically track the wall movement in the spatial reference frame.
The Sliding wall option is appropriate if the wall behaves like a conveyor belt; that is, the surface is sliding in its tangential direction. A velocity is prescribed at the wall and the boundary itself does not have to actually move relative to the reference frame.
|
•
|
For 3D components, values or expressions for the Velocity of sliding wall uw should be specified. If the velocity vector entered is not in the plane of the wall, COMSOL Multiphysics projects it onto the tangential direction. Its magnitude is adjusted to be the same as the magnitude of the vector entered.
|
This section is displayed by clicking the Show More Options button (

) and selecting
Advanced Physics Options in the
Show More Options dialog box. The
Constraints settings can be set to
Default,
Use pointwise constraints,
Use DG constraints, or
Use weak constraints.
Use mixed constraints can be selected when imposing a no slip condition exactly.
|
•
|
Apply reaction terms on can be set to Individual dependent variables (default) or All physics (symmetric). This setting is not available when Use DG constraints is selected.
|
|
•
|
Select Elemental (default) or Nodal under Constraint method. This setting is not available for Use DG constraints or Use weak constraints.
|