Select a Capillary pressure model —
User defined (the default),
van Genuchten, or
Brooks and Corey. The latter two options are only available when there are not more than two phases present in the model.
Select the material to use for each phase. Select Domain material (the default) from the
Fluid list to use the material defined for the domain. Select another material to use that material’s properties.
Enter the Density ρ (SI unit: kg/m
3),
Dynamic viscosity μ (SI unit: Pa·s) and
Relative permeability κr (a dimensionless number between 0 and 1) for each phase. The defaults for the
Density and
Dynamic viscosity are
From material, and
User defined for the
Relative permeability. For
User defined, the default values are 1000 kg/m
3, 0.001 Pa·s. and
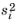
, respectively.
The Relative permeability input fields are only available when the
Capillary pressure model is set to
User defined. In the other cases (
van Genuchten or
Brooks and Corey) the relative permeabilities are defined by the
van Genuchten or
Brooks and Corey model. For the
van Genuchten and
Brooks and Corey model, specify the
Residual saturation sri (dimensionless, default value 0) for each phase.
Select the material to use as porous matrix. Select Domain material (the default) from the
Porous material list to use the material defined for the porous domain. Select another material to use that material’s properties.
The default Porosity εp (a dimensionless number between 0 and 1) uses the value
From material, defined by the
Porous material selected. For
User defined the default is 0.5.
The default Permeability κ (SI unit: m
2) uses the value
From material, as defined by the
Porous material selected. For
User defined the default is the
Isotropic scalar value of
1e-9 m
2. To define a tensor value, select
Diagonal,
Symmetric, or
Full, and enter values or expressions in the matrix.