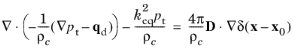Use the Dipole Point Source node to add a dipole point source. A dipole is mathematically a source that corresponds to two monopoles close to each other that are completely out of phase. Dipoles appear when there are fluctuating forces in the medium; for example, a small object that vibrates back and forth. A complex acoustic source may be expanded and approximated by a collection of point sources (
Monopole Point Source, Dipole Point Source, and
Quadrupole Point Source). The dipole point source adds a point source term to the right-hand side of the governing Helmholtz equation such that:
where δ(x − x0) is the delta function in three dimensions and adds the source at the point where
x = x0. The dipole moment vector
D (SI unit: N) depends on the source type selected, as discussed below. In 2D axisymmetric models, the dipole point source is only added to the
z-axis, such that
x0 = (0,0,
z). See
Ref. 5 for details.
For User defined enter a
Dipole moment vector D (SI unit: N). In 2D axisymmetric components enter the
z-component only.
The Power option defines the following dipole moment vector in terms of the free space reference power, the dipole direction, and the source phase