|
•
|
The Compute optical path length check box must be selected in the Geometrical Optics Settings window before solving.
|
|
•
|
|
•
|
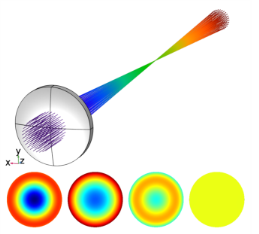
In the Settings window for the Intersection Point 3D data set, Hemisphere must be selected from the Surface type list. The Center is the location of the focus and the Axis direction points from the focus toward the center of the exit pupil.
|
|
In the COMSOL Multiphysics Reference Manual:
|