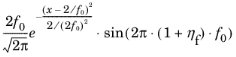Use the Lumped Port node to apply a voltage or current excitation of a model or to connect to a circuit. A lumped port is a simplification of the port boundary condition.
A Lumped Port condition can only be applied on boundaries that extend between two metallic boundaries — that is, boundaries where
Perfect Electric Conductor,
Impedance Boundary,
or
Transition Boundary (Electromagnetic Waves, Frequency Domain interface only) conditions apply — separated by a distance much smaller than the wavelength.
Enter a unique Lumped port name. It is recommended to use a numeric name as it is used to define the elements of the S-parameter matrix and numeric port names are also required for port sweeps and Touchstone file export (for the Electromagnetic Waves, Frequency Domain interface).
Select User defined for nonuniform ports, for example, a curved port and enter values or expressions in the fields —
Height of lumped port hport (SI unit: m),
Width of lumped port wport (SI unit: m), and
Direction between lumped port terminals ah. In 2D axisymmetry,
Coaxial does not support a nonzero azimuthal mode number. The
Azimuthal mode number should be set to zero in the
Out-of-Plane Wave Number section in the settings for
The Electromagnetic Waves, Frequency Domain Interface. When it is modeled in 3D, its geometry has to be a full coaxial shape.
Select Multielement uniform for multi-excitation or -termination of, for example, a coplanar waveguide port or a differential port. The direction of the field in each sub-element of the
Multielement uniform lumped port is defined by the subnodes,
Uniform element.
Select a Terminal type — a
Cable port for a voltage driven transmission line and S-parameter calculation, a
Current driven port, or a
Circuit port.
For Cable select
On or
Off from the
Wave excitation at this port list to set whether it is an inport or a listener port. If
On is selected, enter a
Voltage V0 (SI unit: V), and
Port phase θin (SI unit: rad).
Note it is only possible to excite one Cable port at a time if the purpose is to compute S-parameters. In other cases, for example, when studying microwave heating, more than one inport might be wanted, but the S-parameter variables cannot be correctly computed so if several ports are excited, the S-parameter output is turned off.
For the Electromagnetic Waves, Frequency Domain and Microwave Heating interfaces, the Port Sweep Settings cycles through the ports, computes the entire S-matrix, and exports it to a Touchstone file. When using port sweeps, the local setting for
Wave excitation at this port is overridden by the solver so only one port at a time is excited.
No entry is required if a Circuit terminal type is selected above.
The Calculate S-parameter check box needs to be activated for S-parameter calculation with the Electromagnetic Waves, Transient and Electromagnetic Waves, Time Explicit interfaces, while the
Cable port in the Electromagnetic Wave, Frequency Domain calculates S-parameters automatically.
where the Center frequency f0 defines the location as 2
/f0, the standard deviation as 1/(
2f0), and the modulation frequency
f0. ηf is the upshift ratio for the sinusoidal modulation frequency.
When Calculate S-parameter is checked, enter a
Center frequency f0 for the input modulated Gaussian pulse (SI unit: Hz).
When Calculate S-parameter is checked, enter a
Modulation frequency upshift ratio ηf for the input modulated Gaussian pulse.