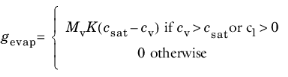This node should be used to model evaporation from and condensation to a solid surface partially covered with liquid water. It adds the evaporation flux to the boundary conditions of Equation 7-4 of
Moist Air (MT Interface) node, and computes the corresponding latent heat source to be added in the heat transfer equation. In addition, it computes the liquid water concentration accumulated on the surface, during evaporation and condensation processes.
where Mv is the molar mass of water vapor (SI unit: kg/mol),
K is the evaporation rate factor (SI unit: m/s),
csat is the saturation concentration of vapor (SI unit: mol/m
3),
cv is the vapor concentration (SI unit: mol/m
3), and
cl is the liquid water concentration on surface (SI unit: mol/m
2).
The latent heat source qevap (SI unit: W/m
2) is obtained by multiplying the evaporation flux by the latent heat of evaporation
Lv (SI unit: J/kg):
With these definitions, gevap is negative when condensation occurs, and positive during evaporation. Whereas the condensation process does not depend on the liquid concentration on the surface, the evaporation process only happens when the (initial or time-dependent) liquid concentration on surface is positive.