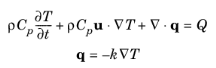This node models heat transfer in shape memory alloys, and accounts for the Martensite and Austenite composition. This feature is designed to be coupled with the Shape Memory Alloy feature of the Structural Mechanics interface which computes the alloy composition from the mechanical and thermal loads. Changes in Martensite and Austenite composition modify the alloys thermal properties (thermal conductivity and heat capacity), and release (from Austenite to Martensite state) or absorb (from Martensite to Austenite state) energy.
This section is available when a temperature-dependent density is used. On the material frame, the density is evaluated onto a reference temperature to ensure mass conservation in the presence of temperature variations. By default the Common model input is used. This corresponds to the variable
minput.Tempref, which is set by default to 293.15 [K]. To edit it, click the
Go to Source button (

), and in the
Common Model Inputs node under
Global Definitions, set a value for the
Volume reference temperature in the
Expression for remaining selection section.
The other options are User defined and all temperature variables from the physics interfaces included in the model.
This section is available when temperature-dependent material properties are used. By default the temperature of the parent interface is used and the section is not editable. To edit the Temperature field, click
Make All Model Inputs Editable (

). The available options are
User defined (default),
Common model input (the
minput.T variable, set to 293.15 [K] by default) and all temperature variables from the physics interfaces included in the model. To edit the
minput.T variable, click the
Go to Source button (

), and in the
Common Model Inputs node under
Global Definitions, set a value for the
Temperature in the
Expression for remaining selection section.
The Martensite volume fraction,
ξ, and the
Density of the alloy (defined for both Austenite and Martensite states) should be set in this section.
In addition, the following options are available for the computation of the Effective conductivity by accounting for both Austenite and Martensite properties:
The default Thermal conductivity kA is taken
From material. For
User defined select
Isotropic,
Diagonal,
Symmetric, or
Anisotropic based on the characteristics of the thermal conductivity, and enter another value or expression. For
Isotropic enter a scalar which will be used to define a diagonal tensor. For the other options, enter values or expressions into the editable fields of the tensor.
The default Heat capacity at constant pressure Cp,A is taken
From material. For
User defined enter a value or expression.
The default Thermal conductivity kM is taken
From material. For
User defined select
Isotropic,
Diagonal,
Symmetric, or
Anisotropic based on the characteristics of the thermal conductivity, and enter another value or expression. For
Isotropic enter a scalar which will be used to define a diagonal tensor. For the other options, enter values or expressions into the editable fields of the tensor.
The default Heat capacity at constant pressure Cp,M is taken
From material. For
User defined enter a value or expression.
If the Heat transfer in alloys check box is selected under the
Physical Model section:
More locations are available if the Heat transfer in alloys check box is selected under the
Physical Model section. For example:
Heat Transfer in Fluids>Shape Memory Alloy