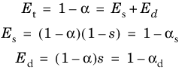At a wall where both specular reflections and diffuse reflections occur it is common to define the scattering coefficient s. This coefficient relates the amount of energy that is specularly
Es and diffusely
Ed reflected to the (total) absorption coefficient
α. The normalized total reflected energy
is Et. The relations between these are
where αs is the specular absorption coefficient and
αd is the diffuse absorption coefficient.
In the Ray Acoustics interface the mixed reflection condition is treated using a Monte Carlo like approach. When a ray hits a mixed wall condition the ray is either diffusely or specularly reflected according to the
Probability of specular reflection γs. This means that the probability plays the role of the scattering coefficient, by setting
γs = 1
− s. The
Specular absorption coefficient and the
Diffuse absorption coefficient should both be set equal to the total absorption
α.