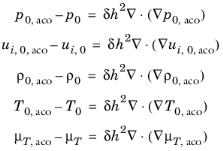If two different mesh or different shape function orders are used in the acoustic and the CFD models a mapping study needs to be used. This is a study that solves an additional set of equations which maps and smooths the background flow CFD variables onto the acoustics mesh. The mapping equations can be set up using the Weak Form PDE interface from the
Mathematics branch. In the most general case the mean background flow pressure
p0, velocity field
u0, density
ρ0, temperature
T0, and turbulent viscosity
μT variables should be mapped onto corresponding variables on the acoustics mesh, for example,
p0,aco,
u0,aco,
ρ0,aco,
T0.aco, and
μT,aco. These new variables should then be used as the model inputs in the aeroacoustics model.
where the term on the right hand side adds smoothing using isotropic diffusion. The amount of diffusion is controlled by the parameter δ (a constant that can be tuned with a typical value of 0.01) and the mesh size squared
h2. The term corresponds to so-called source term stabilization as known from CFD.
In the Weak Form PDE interface define as many dependent variables as necessary and give them the same shape order as the order used for the acoustics (typically all linear). Assume that the source CFD variable for the x-velocity component is
u and the new destination variable is
U0, then the above mapping is achieved with the following
Weak Expression, entered in the user interface:
Notice the use of the withsol() operator, which is an extrusion-like coupling operator that can refer directly to a solution object and parameter value. In this example it is used to fetch data from the CFD mesh, in the solution generated by solver
sol1 and for the parameter value
Ma =
0.1. The
setval() statement is optional. It is important to use such an operator such that the CFD solution is mapped and interpolated correctly to the integration (Gauss) points on the acoustics mesh.