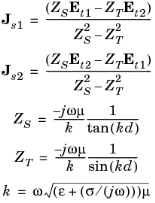The Transition Boundary Condition is used on interior boundaries to model a sheet of a medium that should be geometrically thin but does not have to be electrically thin. It represents a discontinuity in the tangential electric field. Mathematically it is described by a relation between the electric field discontinuity and the induced surface current density:
Select an Electric displacement field model —
Relative permittivity,
Refractive index (the default),
Loss tangent, loss angle,
Loss tangent, dissipation factor,
Dielectric loss,
Drude-Lorentz dispersion model,
Debye dispersion model, or
Sellmeier dispersion model. See the
Wave Equation, Electric node,
Electric Displacement Field section, for all settings.
Enter a Thickness d (SI unit: m). The default is 0.01 m.