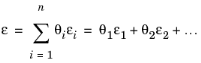where εi is the relative permeability of the material i.
The effective permeability calculated by Volume Average, Permittivity is the upper bound, the effective permeability calculated by
Volume Average, Reciprocal Permittivity is the lower bound, and the
Power Law average gives a value somewhere in between these two.