The double dogleg method (Ref. 22) is available for stationary problems. It is a Newton trust region method and can as such adjust the direction as well as the step length when solving the nonlinear equation
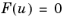
,
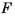
:
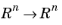
.
subject to 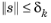 . Here the size of the step s
. Here the size of the step s is required to be bounded by the trust region radius
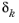
. Both the Cauchy point — that is, the minimizer of
m in the steepest descent direction — and the Newton point are utilized. In each iteration the algorithm dynamically adjusts the size of the trust region depending on the predicted decrease of
m compared to the actual one. The double dogleg step is then given by a certain convex combination of the Cauchy step (steepest descent direction) and the Newton step. For difficult problems you can choose to start the computation by a damped Newton step. Enter the damping factor between 0 and 1 in the
Initial damping factor field. The algorithm terminates if the norm of the scaled residual is less than the given tolerance,
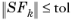
. You can choose the type of scaling in the
Residual scaling list. See the
Fully Coupled Method and Termination settings.