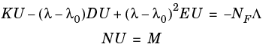Here LinearType is any of the allowed linear solver feature types.
For both linear and nonlinear problems, the eigenvalue problem is that of the linearization about a solution U0. If the eigenvalue appears nonlinearly, COMSOL Multiphysics reduces the problem to a quadratic approximation around a value
λ0 specified by the property
eigref. The discretized form of the problem reads
where K,
D,
E,
N, and
NF are evaluated for
U = U0 and
λ = λ0.
Λ is the Lagrange multiplier vector, and
λ is the eigenvalue. The eigenvalue name can be given by the property
eigname. The linearization point
U0 can be given with the property
U. The shift, described below, is compensated according to the linearization point for the eigenvalue. Therefore, changing the linearization point has no effect at all for linear or quadratic eigenvalue problems. The eigenvalue search method can be manual or a region in the complex plane (controlled by the property
eigmethod).
The feature eigenvalue accepts the following property/value pairs:
Specify where to look for the desired eigenvalues with the property shift. Enter a real or complex scalar; the default value is 0, meaning that the solver tries to find eigenvalues close to 0.
If Solfile is
on, the solution is stored on a temporary file. The temporary file is stored in the temporary directory created at startup. You can decide the temporary directory with the
-tmpdir switch. A part of the solution is stored in memory in a few
blocks (usually 1–5 blocks reside in memory). The maximum block size (in megabytes) can be controlled with the property
Solfileblock.