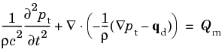
|
See Pressure Acoustics for details of the fluid model equations.
|
|
•
|
Select User defined to enter a value or an expression for the absolute pressure (SI unit: Pa) in the field that appears. This input is always available.
|
|
•
|
In addition, select an absolute pressure defined by a Fluid Flow interface present in the model (if any). For example, select Absolute pressure (spf) to use the absolute pressure defined by a Laminar Flow interface spf. This allows the use of a system-based (gauge) pressure, while automatically including the reference pressure in the absolute pressure.
|