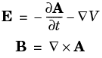The variable transformation of the potentials is called a gauge transformation. To obtain a unique solution, choose the gauge—that is, put constraints on
Ψ that make the solution unique. Another way of expressing this additional condition is to put a constraint on
∇ · A. A vector field is uniquely defined up to a constant if both
∇ · A and
∇ × A are given. This is called
Helmholtz’s theorem.